Every cell (of eukaryotes or prokaryotes) has one or more DNA (or RNA) polymer molecules that need to duplicate in order the cell duplication to take place. This is what DNA Replication -aka DNA Synthesis- succeeds.
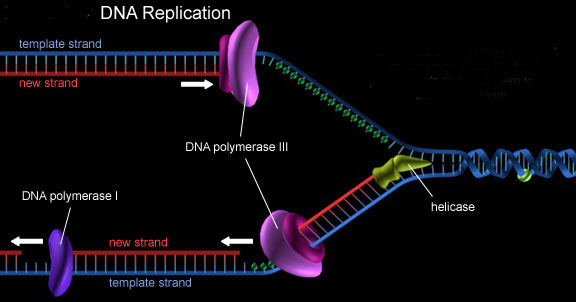
In the eukaryotes (organisms with cell that have nucleus) the DNA is formed in two strands, each composed of units called Nucleotides. The two strands look like two chains that form the DNA Double Helix. The DNA Replication Process is capable of opening the Double Helix and separating the two strands. Then the two strands are copied. As a result two new DNA molecules are created. The next step is the cell division. After that a daughter cell is created. In its nucleus lies a copy of the parental DNA.
Follow the links in the left menu in order to find more info about the DNA Replication Process.

In the eukaryotes (organisms with cell that have nucleus) the DNA is formed in two strands, each composed of units called Nucleotides. The two strands look like two chains that form the DNA Double Helix. The DNA Replication Process is capable of opening the Double Helix and separating the two strands. Then the two strands are copied. As a result two new DNA molecules are created. The next step is the cell division. After that a daughter cell is created. In its nucleus lies a copy of the parental DNA.
Follow the links in the left menu in order to find more info about the DNA Replication Process.
No comments:
Post a Comment